Last revised: January 13, 2025
Microsoft Fabric and Databricks: Two SaaS offerings that host a variety of analytical workloads that help enable key use cases like data science, data engineering, and machine learning & AI. While commonly used separately, these platforms can come together to meet almost all your data demands while providing an array of experiences that can fit the need of a user at any level of the technical spectrum.
In this article, we dive into analyzing these platforms, focusing on their strengths, use cases, and cost-effectiveness. If you are weighing options for big data processing, machine learning, and seamless integration, understanding how these platforms work is essential. Discover which platform aligns best with your data aspirations and constraints, or when it might be best to combine the two.
Key Takeaways
- Microsoft Fabric serves as a user-friendly all-in-one analytics platform leveraging Azure technologies, ideal for business users, while Databricks excels in big data processing and machine learning across major cloud providers, catering to more technical data professionals.
- Both Fabric and Databricks provide robust capabilities for data engineering, with Fabric emphasizing ease of use and integration, and Databricks offering advanced capabilities for complex data processing tasks.
- Security, compliance, and flexible pricing models are integral to both platforms, with Fabric offering a pay-as-you-go plan and Databricks using a usage-dependent pricing model, ensuring businesses can align costs with their specific needs and data security standards.
- Depending on specific requirements, a combined model that leverages the unique strengths and capabilities of Fabric and Databricks may be practical. With Azure Databricks, enterprises can harness the power and flexibility of Databricks while leveraging the native integrations available within the Azure platform.
Exploring Microsoft Fabric and Databricks
Within the ever-evolving world of data analytics, two titans stand out: the recent entrant, Microsoft Fabric, and the reigning champ, Databricks. These platforms are not just tools; they are the architects of insightful data products-serving distinct yet complementary roles in the domain of big data management and analytics.
Microsoft Fabric distinguishes itself as a comprehensive all-in-one analytics platform, intricately woven using Microsoft Azure core technologies. On the other hand, Databricks excels as an analytics powerhouse, renowned for its prowess in big data processing and machine learning. Together, they offer a lot of versatility – whether it is storing data in OneLake and using Databricks to process that data or using Databricks to ingest raw data and shortcutting it to Microsoft Fabric, your data strategies can become more creative and reach new heights.
The Core of Microsoft Fabric
At the heart of its operations, Microsoft Fabric functions as a cloud-based platform embodying simplicity and integration. As a SaaS solution, it caters to a spectrum of users by embracing a no-code/low-code approach, ensuring that from the novice to the seasoned professional, everyone can access the data they need in a single-pane of glass. When comparing Microsoft Fabric vs other platforms, its user-friendly nature sets it apart.
Fabric’s mastery lies in its seamless integration with Azure technologies, including Azure Data Factory, creating a unified environment that supports open data formats like Parquet and Delta Lake. This is a meaningful change for those who seek agility and interoperability in their data solutions. Ultimately, Fabric provides the most flexibility with the least amount of administrative overhead.
Databricks: The Unified Analytics Powerhouse
Databricks positions itself as a cloud-agnostic platform that uses a highly optimized version of Apache Spark to offer an all-encompassing analytics ecosystem. The platform is built for collaboration that allows users to tackle complex data problems and manage data at granular level thanks to the capabilities of Unity Catalog. In contrast to Microsoft Fabric, Databricks offers integration with various analytics tools (Fivetran, Informatica, etc.) and Customer Experience ecosystem partners directly within their platform, allowing users of all personas to leverage their existing tools to bring data into the Databricks platform.
Analyzing Data Engineering Capabilities
In further exploring these platforms’ technical strengths, we analyze their data engineering capabilities:
As a SaaS offering, Microsoft Fabric eliminates the provisioning requirements of Microsoft Data Engineering tools like Azure Data Factory and Synapse. Instead, Fabric simplifies the Data Engineering experience by tailoring it to a specific “persona”. Within the user-friendly interface, a user need only to select Data Factory or Synapse as a persona, with the former being a tailored experience for low code/no code users while the latter supports a more seasoned professional.
Databricks’ core competency, in contrast, has always been focused around its data engineering capabilities. The data engineering experience on Databricks is built around its notebooks and workflows, with the biggest benefit being the granular controls Databricks offers when managing the clusters that run these notebooks.
Data Ingestion and Integration
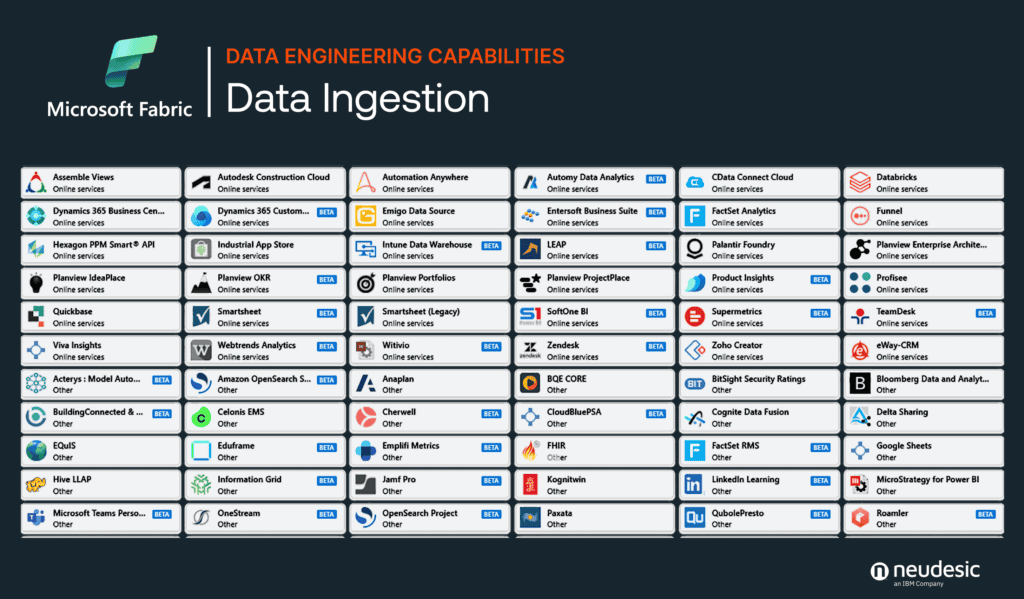
A unified platform’s usefulness rests in its proficiency to ingest and incorporate data efficiently. Microsoft Fabric rises to the challenge with its data engineering tools by offering streamlined data ingestion from a multitude of sources and facilitating seamless integration with a no-code/low-code paradigm. When using the previously mentioned Data Factory persona, a user can leverage the Copy Data Activity to select a data source to ingest directly through the user interface and is provided with a host of additional options when using the same persona but ingesting data via a Data Flow.
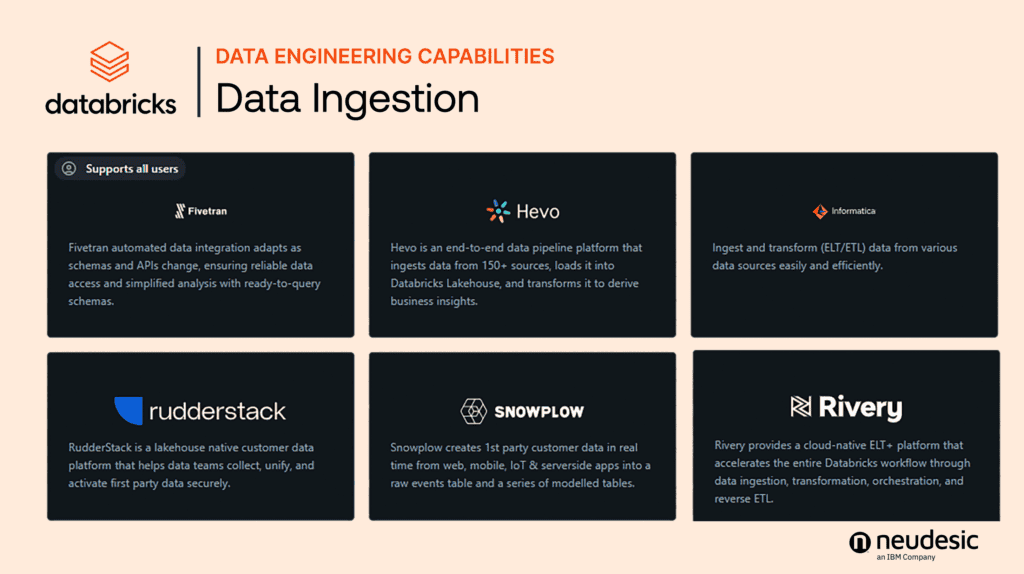
Databricks complements this with its prowess in constructing declarative data pipelines via Delta Live Tables, making it a stalwart for those who navigate the big data seas with precision and control. The platforms’ approaches to data integration not only reflect their core strengths but also cater to the diverse skill sets of data professionals. If a company has an existing data analytics tool being used for ingestion, Databricks makes it easy to integrate the tool into its Unity Catalog environment via their Partner Connect feature. Existing tools such as Fivetran and Informatica can be easily called within the Databricks UI and used to ingest data with existing processes.
Data Transformation and Storage
Beyond the scope of ingestion, one enters the transformative domain of data storage and manipulation. Here, Microsoft Fabric introduces its data warehouses components and OneLake storage, offering a streamlined path from data lakes to insights. On the other side, Databricks employs a serverless lakehouse architecture, a scalable and efficient approach in the data storage universe.
Both platforms flex their muscles in data transformation, yet their methodologies diverge, presenting a choice between the structured world of Fabric and the fluid architecture of Databricks.
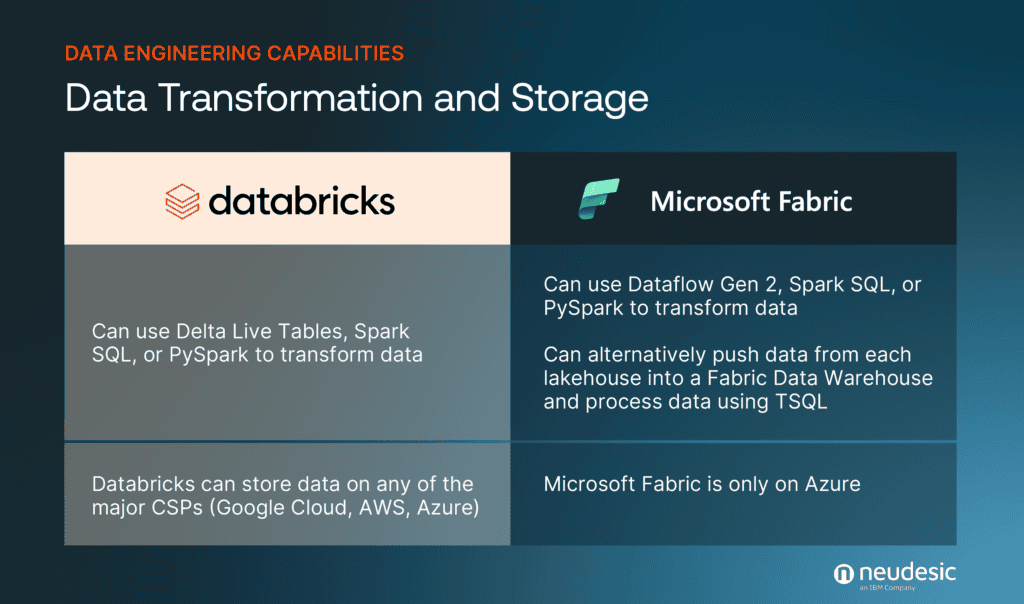
Databricks Delta Live tables allow users to define streaming tables which in turn makes the data transformation experience more accessible to users who may only have experience transforming data via SQL scripts. If not using Delta Live Tables, storing data in Unity Catalog makes data easily accessible to the other language types (Scala, Python, R) for further data processing.
Microsoft Fabric offers Data Transformation capabilities via Synapse notebooks and Data Flows. Fabric Data Flows offer a no code experience allows users to curate their data transformations through a set of activities that are offered through a simple dropdown. For extremely new users, the use of Microsoft Copilot in Fabric could help them develop a pipeline fairly quickly simply by defining their transformation needs in a natural language query and allowing AI to build the pipeline for them.
Below is a summary of both platforms’ Data Transformation capabilities:
Data Science and Machine Learning Showdown
As the discussion transitions to data science and machine learning, both platforms offer similar experiences Databricks, with its robust set of collaborative tools, is a popular platform for complex data science endeavors. Its capabilities in advanced analytics and machine learning are a testament to its strength.
In Microsoft Fabric, the Data Science persona allows you to easily create new ML Model objects and group those objects within an Experiment, allowing you to track the development of multiple models.
Collaborative Data Science Notebooks
The cooperative data science notebooks provided by Microsoft Fabric and Databricks narrate their individual tales of synergy and innovation. Fabric’s notebooks foster a collaborative environment with features that allow multiple users to co-edit and contribute simultaneously, thus democratizing the data science process.
On the flip side, Databricks Notebooks streamline the development experience, offering a rich environment that seamlessly connects to the Lakehouse Platform, enabling rapid iteration and sharing of work across teams, personas, and skill levels.
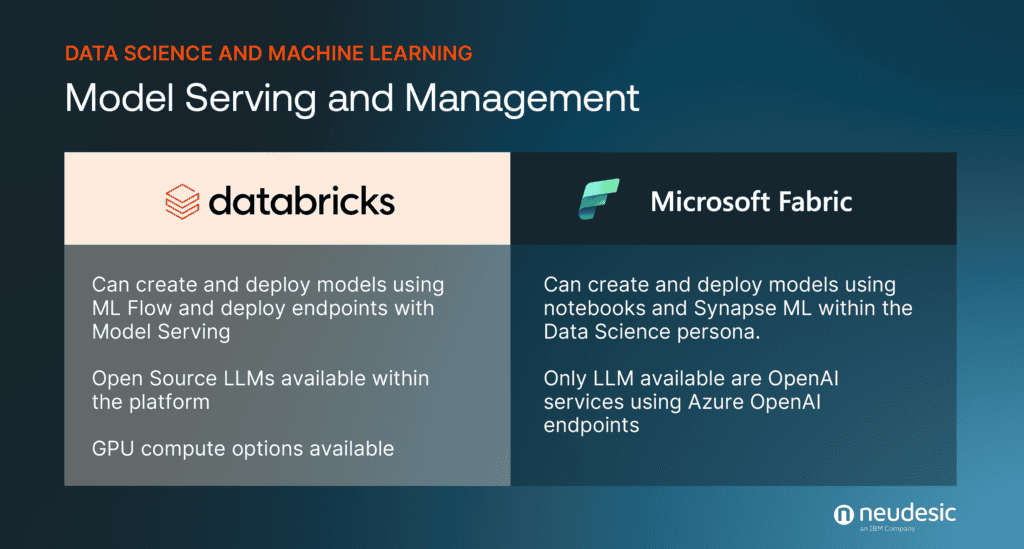
Model Serving and Management
In terms of model serving and management, both platforms impress with scalable solutions tailored to meet the demands of contemporary businesses. Databricks, with its unified interface for deploying AI models as REST APIs, offers a sophisticated suite of tools for workflow orchestration and observable execution.
Microsoft Fabric, not to be outdone, enables efficient model management through its notebook integrations and tracking capabilities, ensuring that data scientists can refine their models with precision.
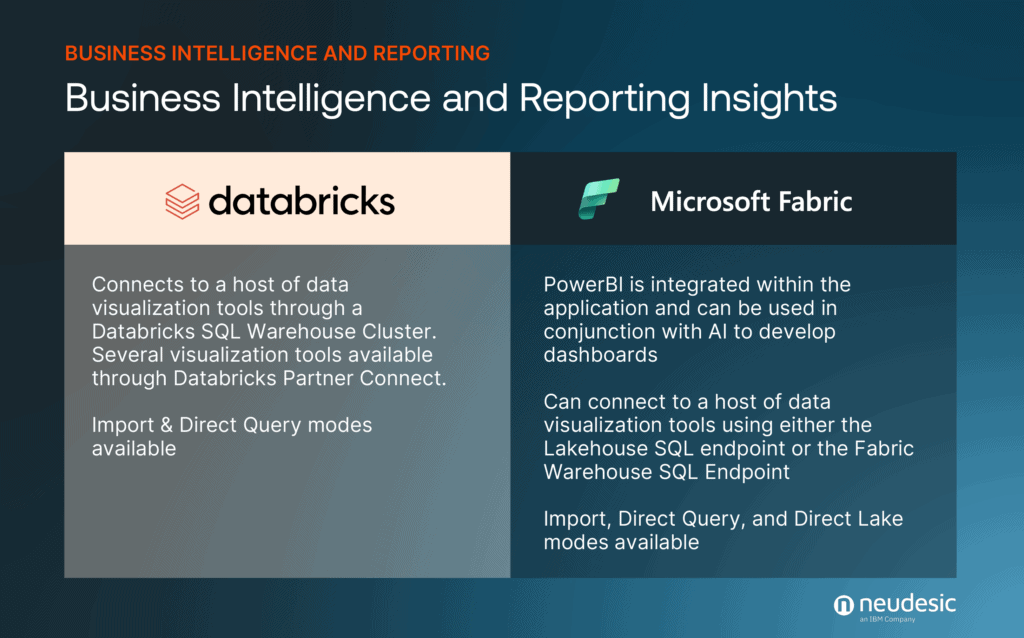
Business Intelligence and Reporting Insights
As we shift our focus towards the realm of business intelligence and reporting, the insights derived from Microsoft Fabric and Databricks shed light on the way forward. Both platforms integrate seamlessly with a host of visualization tools, offering real-time analytics capabilities that empower users to craft reports with the latest data architecture trends in mind.
The clarity and context provided by these tools are invaluable for businesses looking to make informed decisions swiftly.
Real-time Analytics and Intelligence
The race for real-time analytics and intelligence is a competitive field where both Microsoft Fabric and Databricks outperform. Their capabilities in data streaming and processing with minimal latency enable immediate insights and data-driven decision-making.
Databricks stands out with its Serverless SQL Warehouse , which offers a powerful, scalable solution for real-time analytics. Microsoft Fabric has similar capabilities through its Real-Time Intelligence persona, where you can use an Eventhouse to rapidly load structured, unstructured and streaming data for querying or use a KQL Queryset to produce shareable tables and visuals.
Seamless Integration with Office 365
Microsoft Fabric offers a seamless integration with Office 365, providing a unified analytics platform that brings together data from across the Microsoft ecosystem. The integration with Microsoft 365 data creates a cohesive environment where insights from:
- Teams
- Outlook
- SharePoint
- and other sources
can be leveraged to generate comprehensive business intelligence, ensuring data reliability.
Pricing Model Comparison
In the sphere of data analytics, cost considerations hold equal importance to the capabilities of the platforms themselves. The pricing model Microsoft Fabric offers-pay-as-you-go hourly or monthly-provides flexibility and simplicity, allowing businesses to scale their data solutions in alignment with their usage patterns.
Databricks, with its usage-dependent pricing model, presents a different approach, charging based on resource consumption and offering the potential for cost optimization based on workloads. This is a highly flexible model that allows cost to be tailored to the exact requirements of your production workloads.
Microsoft Fabric’s Subscription Details
Peering into the subscription landscape of Microsoft Fabric reveals an enticing offer-a free trial for Power BI users, extending the platform’s reach and allowing businesses to explore its data engineering capabilities risk-free.
With a pricing structure based on capacity units, Microsoft Fabric caters to a range of business sizes and needs, offering flexibility and scalability within its subscription models.
Databricks’ Usage-Dependent Pricing Model
The economics of Databricks’ usage-dependent pricing model present a calculated approach where costs are tied to the runtime hours of virtual machines. . This model speaks to the efficiency and scalability needs of businesses, ensuring they only pay for what they use, thereby enabling a more tailored allocation of resources.
Security and Compliance Standards
In an environment where data security and compliance are uncompromisable, both Microsoft Fabric and Databricks maintain stringent standards and proudly hold certifications such as SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA. These certifications are a testament to their commitment to safeguarding data and ensuring the integrity of their platforms.
Encryption and Authorization Protocols
The encryption and authorization protocols deployed by Microsoft Fabric and Databricks are the bedrock of their security architectures. With comprehensive data encryption and robust authentication features, both platforms ensure that data remains secure, whether at rest or in transit, while also providing granular control over access permissions.
Achieving Compliance with Major Cloud Providers
Navigating the compliance landscape, Microsoft Fabric stands out with a litany of certifications, showcasing its ability to meet and exceed the expectations of major cloud providers. This dedication to compliance is essential for businesses that demand the highest standards of data security and governance.
Summing it up: Choosing the Right Platform for Your Data Needs
The mission to choose the appropriate data platform depends on matching specific data requirements with the unique strengths of Microsoft Fabric and Databricks. For those seeking an integrated Azure-based solution, Microsoft Fabric offers a compelling proposition, while Databricks stands as the champion of big data processing and machine learning for more complex data projects.
Assessing Your Data Squad and Project Goals
Understanding the expertise of your data squad and the objective of your project is paramount in choosing between Microsoft Fabric and Databricks. Fabric’s beginner-friendly ecosystem is inviting for those taking their first steps into data analytics, whereas Databricks is the playground for seasoned data scientists seeking deeper data exploration and big data analytics.
Generative AI (GenAI) Capabilities
Both platforms offer GenAI capabilities and choosing the best one will be entirely dependent on your use case. If you’re looking to develop chat-bot like applications for end users within your enterprise, then Databricks will be the better option.
For example, with their Mosaic AI Agent Framework, you will be able to invite subject matter experts to quickly assess the quality of a GenAI application and allow you to iterate on your application to ensure that the answers your application is generating meets the standards of the enterprise.
Databricks also offers a robust toolset for the development of GenAI applications supporting everything from prompt engineering and RAG to fine tuning and pretraining. Databricks integration with Hugging Face and flexible Model Serving capabilities allow you to select any model that works for your business whether proprietary or open source.
Databricks has also recently introduced AI/BI Genie, which is a feature that allows teams to interact with their data using natural language. Analysts can connect a collection of Unity Catalog tables to a Genie space and ask questions and generate visuals to help users better understand operational data.
Microsoft also offers similar capabilities with Azure AI Studio, but this experience (as of this writing) is not yet integrated with Microsoft Fabric and would have to be maintained separately. Fabric’s Gen AI capabilities separate itself from Databricks by catering the Microsoft Copilot experience to the different personas they offer within Fabric.
For example, if you are looking to quickly develop a data pipeline, the Copilot experience through the Data Factory persona will allow you to do so. As a Data Engineer, you will be able to use natural language to generate code for you (Databricks offers something similar through their Databricks Assistant), and if you’re a Power BI user, natural language can be used to create entire reports/dashboards for you by simply using natural language.
Similar to Databricks’ Genie spaces, Microsoft recently announced a Fabric feature called AI skill. This feature allows you to create a ‘skill’ which allows you to connect either a lakehouse or data warehouse to a language model and ask questions of your data. These AI skills offer several configuration options that allow users to customize the language model behavior to better suit specific use cases.
In addition, if you really want to push the value of Fabric and GenAI, you can also create custom copilots with Microsoft’s low-code/no-code Copilot Studio solution.
Balancing Features with Budget Constraints
Striking a balance between desired features and budget limitations is a vital factor in the process of platform selection. Both Microsoft Fabric and Databricks offer specialized features that cater to advanced analytics and real-time streaming, yet their respective pricing models and integration capabilities must be weighed against the financial boundaries of the organization.
When you might want to use Microsoft Fabric
If you have a small, inexperienced data squad and minimal interest in managing infrastructure, then Fabric will be the choice for you. If many of your source data sits in a SQL-based data warehouse, then migrating to Fabric will be a smooth transition as Fabric has native TSQL and stored procedure compatibility through their Fabric Data Warehouse.
When you might want to use Databricks
If your data team consists of experienced professionals, then Databricks will be the choice for you. Databricks would also be a natural selection if you are using a host of different vendors to accomplish your data goals. Many of these vendors can be accessed within the Databricks platform and will allow you to easily write data into Unity Catalog. The auto scaling capabilities of Databricks clusters, combined with the many different cluster offerings available, makes the processing of many different big data use cases much simpler. Additionally, the Databricks platform offers a tightly integrated feature set that accelerates collaboration when multiple teams or personas need to operate out of a single data stack.
Better together
Combining the two platforms could allow you to reap the benefits of both while still offering the user experience flexibility that keeps all data users engaged and create a greater sense of data ownership. Fabric’s Dataflow Gen2, with all its native connectors, offers a low code alternative to connect to a larger set of data sources, which in turn reduces the ingestion time and allows a larger swath of data professionals to be involved in the process. Once ingested a more seasoned professional can then use Databricks, and all its processing capabilities, to process the data as needed before exposing the data to PowerBI users via a Databricks SQL endpoint.
Databricks and Microsoft recently announced Unity Catalog Mirroring in Fabric, which allows customers to read data managed by Unity Catalog from Fabric workloads. Using Fabric to read Unity Catalog data does not require any data movement and replication, meaning any changes made in Databricks is reflected immediately in Fabric, highlighting how these 2 platforms work better together to enhance the user experience.
Summary
We’ve traversed the intricate landscapes of Microsoft Fabric and Databricks, weighed their capabilities, and measured their cost implications. Whether seeking seamless integration with Azure services or delving into the depths of big data analytics, the platform you choose should align with your team’s expertise, project goals, and financial considerations. Embrace the analytics adventure ahead, and let the data lead you to new discoveries and successes. Need help, we have Fabric workshops and Databricks experts to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Microsoft Fabric’s pricing model differ from Databricks’?
Microsoft Fabric’s pricing model differs from Databricks’ by employing a pay-as-you-go model based on capacity units, offering flexibility with hourly or monthly rates, whereas Databricks’ pricing is usage-dependent and scales costs according to virtual machine usage, runtime hours, and data storage.
Can Databricks handle real-time analytics, and how does it compare to Microsoft Fabric?
Yes, Databricks supports real-time analytics through data streaming and its SQL serverless data warehouse, making it a powerful and scalable solution. Microsoft Fabric also offers real-time analytics capabilities, making them both competitive in this arena.
What security certifications do Microsoft Fabric and Databricks hold?
Microsoft Fabric and Databricks hold security certifications such as SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA, showcasing their dedication to strict security and compliance standards.
Is Microsoft Fabric suitable for beginners in data analytics?
Yes, Microsoft Fabric is suitable for beginners in data analytics as it is designed to be beginner-friendly with its no-code/low-code options and integrated tools.
Can I integrate Microsoft Fabric with Office 365 for business intelligence purposes?
Yes, you can integrate Microsoft Fabric with Office 365 to gain comprehensive business insights from Microsoft 365 sources like Teams, Outlook, and SharePoint.
Related Posts